How Does It Work?
A Bright CMS is built to separate concerns into 3 parts: the model, the view, and the controller (MVC). The model is resposible for loading, retrieving, and altering data; the view is responsible for the presentation of the data; and the controller is responsible for choosing the data interactions and view elements used to ultimately build the pages.
In A Bright CMS, the model and view are completely decoupled from one another, and can only interact with the help of the controller, which gathers data and feeds it into the view. In such a scenario, the controller is known as "mediating controller" or "adapter."
Below is a simplified diagram of the application flow:
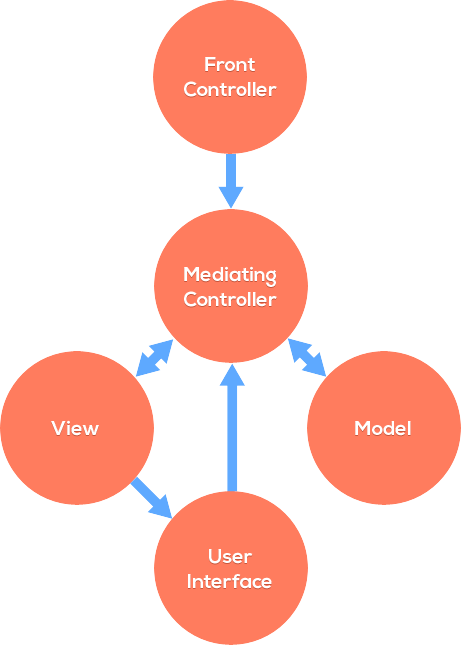
Incoming requests are handled and routed through a front controller which finds the appropriate mediating controller and loads it. The mediating controller loads a view and model object as dependencies.
The mediating controller then calls all the methods it needs from the model to ready the data, builds the view with the view methods, and then sets the data into view properties which are ultimately rendered into the user interface.
The user interface represents the state of the application or website that the user can then see and interact with. Requests or changes made by the user are then sent back to the mediating controller (all the way to the front controller actually, if we’re not using AJAX) where the process begins again.
